What is Hardness of Materials? - Definition from Corrosionpedia

The hardness of a material is defined as its ability to withstand localized permanent deformation, typically by indentation.
Learn MoreWhat is a Hardness Test? - Definition from Corrosionpedia

2018. 6. 1. · A hardness test is a method employed to measure the hardness of a material. Hardness refers to a material’s resistance to permanent indentation. There are numerous techniques to measure hardness and each of these tests can identify varying hardness values for a single material under testing. Hence, hardness test as a method can be dependent
Learn MoreEngineered dental coating exceeds hardness of natural tooth enamel

As the hardest tissue in the human body, enamel is not an easy material for engineers to mimic, but doing so could mean big things in materials science and regenerative medicine. Researchers are
Learn MoreWhat Is Hardness & Types Of Hardness Tests? - Material

Hardness testing is a quantitative test method. In metallurgical science, the hardness value of a material is directly related to the type of microstructure. Ferrite is softer while martensitic is a
Learn MoreTowards the theory of hardness of materials. - arXiv
Center for Computational Sciences, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York for predicting the hardness of a material on the basis of its crystal
Learn MoreHardness - Definition, Measurements, Properties, Methods and FAQs - VEDANTU

Answer: hardness is a measure of a material's resistance to being scratched and is measured using various experimental techniques, including the rockwell tests, barcol test, durometer test, brinell test, mohs test, and vickers and knoop tests. Therefore, the values obtained often depend on the testing method of the knoop diamond.
Learn More5 Ways to Measure the Hardness of Materials - Corrosionpedia

Developed by German geologist and mineralogist, Friedrich Mohs, the hardness of a material is determined by observing whether its surface can be scratched by another material of known hardness. Numerical values are assigned to this property by ranking minerals along a hardness scale (the Mohs scale) that is comprised of 10 minerals.
Learn Moreredirected from Hardness (materials science

Synonyms for Hardness (materials science) in Free Thesaurus. Antonyms for Hardness (materials science). 49 synonyms for hardness: firmness, toughness,
Learn MoreMaterial Hardness Review - Engineers Edge

Hardness is the property of a material that enables it to resist plastic deformation, penetration, indentation, and scratching. Therefore, hardness is important from an engineering standpointbecause resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
Learn MoreHardness Properties | Materials engineering, Tensile, Oil and

Hardness Properties · Hardness is the property of a material enabling it to resist plastic deformation, usually by penetration of another object. · More like this.
Learn MoreThe contributions of David Tabor to the science of indentation

D. Tabor: Indentation hardness and yield properties of solids, in Physics of Materials: Festschrift for Walter Boas, edited by D.W. Borland (
Learn MoreHardness (materials science) - definition of Hardness (materials
hard•ness (ˈhɑrd nɪs) n. 1. the state or quality of being hard. 2. that quality in water that is imparted by the presence of dissolved salts, esp. calcium sulfate or bicarbonate. 3. the comparative ability of a substance to scratch or be scratched by another. 4. the measured resistance of a metal to indention, abrasion, deformation, or machining.
Learn MoreHardness of Materials | The Scratch Test | Science Experiment

Objects around us are made up of different materials. Different materials may have similar or different properties. One property of materials is hardness. Ha
Learn MoreRockwell hardness test - tec-science

In the Rockwell hardness test, an indenter is pressed into the material to be tested. The indentation depth serves as a measure of the hardness!
Learn MoreWhat Is Hardness & Types Of Hardness Tests? - Material Welding

Hardness testing is a quantitative test method. In metallurgical science, the hardness value of a material is directly related to the type of microstructure. Ferrite is softer while martensitic is a hard microstructure. In industries and laboratories, myriad types of hardness testing are performed to meet different sectors, code & standards
Learn MoreHardness, strength, and toughness of materials

2020. 11. 27. · Engineers and scientists were able to predict the reaction of materials when subjected to forces at different levels. This has also allowed the classification of materials
Learn MoreThe hardness of materials and life applications on it

Hardness is the resistance of a material to deformation, indentation or penetration by drilling, abrasion, impact or scratching, Hardness is measured by hardness tests such as Brinell, Rockwell, Knoop or Vickers tests, and there is no standard hardness scale. The hardness of alloy is the diameter of the dent an alloy measured when 1 kg of
Learn Morematerial science - Is there any empirical relation between hardness and

I will restrict my answer to common engineering materials from which useful objects could be fashioned, where hardness would be a useful attribute. This excludes metals that catch fire spontaneously in air, since it would be injudicious to make cars and airplanes out of them. Hardness is a measure of how difficult it is to indent a material
Learn MoreHardness (materials science) | definition of Hardness (materials

hard'nes ), 1. The degree of firmness of a solid, as determined by its resistance to deformation, scratching, or abrasion. See also: hardness scale, number. 2. The relative penetrating power of a beam of x-rays, used both within the diagnostic range of energy and in radiation therapy; expressed in terms of half-value layer.
Learn MoreWhat is Hardness - Definition | Material Properties

In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Hardness is probably the most poorly defined material property because it may indicate resistance to scratching, resistance to abrasion, resistance to indentation or even resistance to shaping or l See more
Learn MorePDF Hardness Testing of Materials - Materials Education (MatEdU)PDF
Hardness is measurement of a material's ability to withstand permanent deformation under an applied (known) force. It's important to have standardized techniques in measuring a materials hardness in order to obtain accurate measurements for comparison Three typical hardness testers " Brinell " Rockwell " Vickers Dial Face Indenter
Learn MoreTypes of Hardness - Materials - Nuclear Power

In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching.Hardness is probably the most poorly defined material property because it may indicate resistance to scratching, abrasion, indentation, or even resistance to shaping or localized plastic deformation. Hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because
Learn MoreWhat does hardness mean? What is its importance in materials science

Answer (1 of 4): Hardness is the surface property of a material that allows it to resist penetration of by another material. For example: a diamond is harder than steel, so a diamond can scratch the steel, but not vice-versa. The application is a file coated with diamond grains will allow you to
Learn MoreHardness (materials science

Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds. However, the behavior of solid materials under force is complex, resulting in
Learn MoreWolfram|Alpha Examples: Material Hardness

Material Hardness. Material hardness is measured using a variety of scales in research as well in industrial applications. The choice of scale depends on the level of hardness needing measured. The Mohs hardness scale is one of the more commonly recognized and was designed to measure the hardness of minerals by using one mineral to scratch another.
Learn MoreEverything You Need to Know About Hardness of Materials
Where, F – force, N. D – indenter diameter, mm. d – indentation diameter, mm. Rockwell Hardness test. This is another common type of hardness test. The kind of material tested
Learn MoreHistorical origins of indentation hardness testing

An issue that has long been of interest is the relation of hardness to simpler measures of material strength, particularly the tensile strength. The review will
Learn MoreHardness (materials science) - The Free Dictionary

hardness · 1. the quality or condition of being hard · 2. (Minerals) one of several measures of resistance to indentation, deformation, or abrasion. See Mohs
Learn MoreMetal Properties: Hardness, Toughness, & Strength
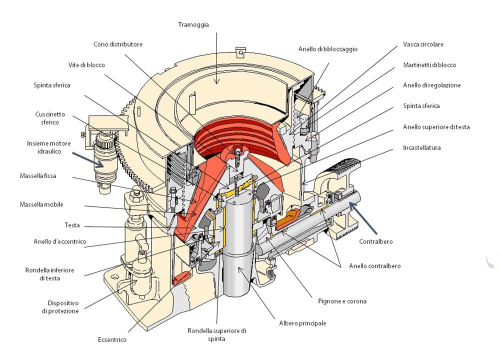
Metal Properties: Hardness, Toughness, & Strength {Infographic} · Hardness: A material's ability to withstand friction, essentially abrasion
Learn MoreHardness measurement | Material Science and Metallurgy
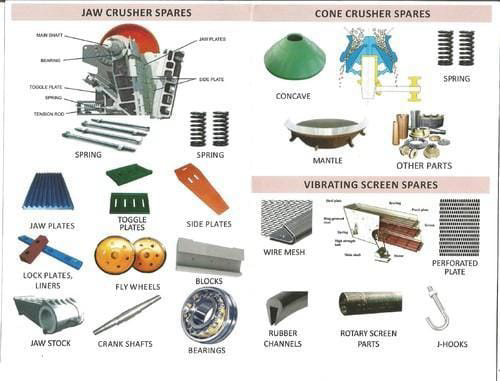
Indentation testing can only be used on materials that undergo plastic deformation such as metals and thermoplastic polymers. Moh's scale of
Learn MoreHardness - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Hardness is the ability of a material to resist deformation, which is determined by a standard test where the surface resistance to indentation is measured.
Learn More

Leave A Reply